THIS IS VITA
Reproductive Medicine - Gynecology – Urology
THIS IS VITA
Reproductive Medicine – Gynecology – Urology
FECUNDACIÓN IN VITRO (FIV)
In vitro fertilization is an assisted reproduction technique that help couples with fertility disorders to achieve pregnancy.
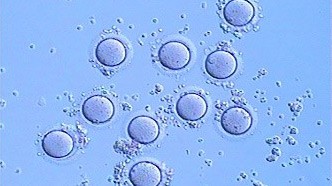
After a complete medical evaluation of the couple and an assessment of the pregnancy-associated risks for the patient, we proceed to stimulate her ovaries with a higher concentration of the natural hormones, in search for the development of not only one but several eggs; this is known as controlled ovary stimulation, a treatment with a duration of 10 to 12 days.
Then, under sedation, we proceed with a transvaginal ovarian puncture for egg recovery. Once we have obtained the egg and the maturation is confirmed, we proceed to set them in contact with the partner`s sperm.
There are two techniques to achieve sperm fertilization of the egg:
One is known as direct insemination or conventional in vitro fertilization, which consists is exposing the egg to a determined number of sperm. This is indicated when the seminal sample is normal.
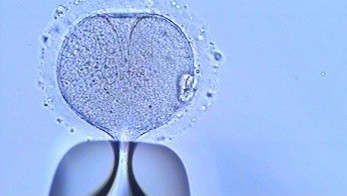
The second is the intracytoplasmic injection (ICSI) that consists in introducing the sperm into the egg cytoplasm. This is indicated when the seminal sample is altered.
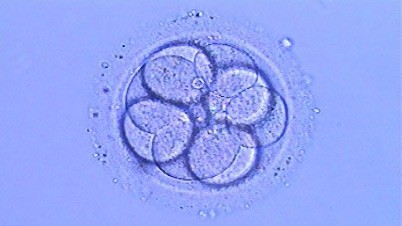
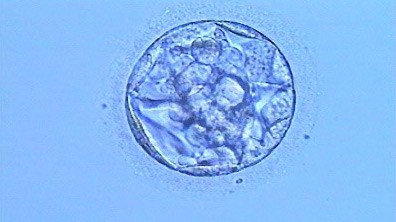
Monitoring of the embryo is done in a daily basis. They are in a special and protected microenvironment which allow them to grow; after three days, depending on certain characteristics, we chose those embryos which we consider optimal to be transferred into the patient`s uterus. We transfer one or a maximum of two embryos (to diminish the probability of multiple pregnancy).
After the embryo transfer, a three-day rest is recommended and on day twelve to fourteen, a pregnancy test is carried out. During these days, patients must take medication that help them maintain the gestation during its initial stages; a permanent communication between Vita and the patients is part of the treatment support. In some cases, we obtain optimal embryos that are not transferred but stored -with a technique known as embryo vitrification-, allowing the couples the possibility of a future second pregnancy or a repetition of the process in case of failure (avoiding all the initial steps of the whole process).